Middle and upper back pain
Contents:
The thoracic spine is the longest section of the spine with 12 thoracic vertebrae. It is responsible for the mobility of the trunk. The cervical spine is the most flexible part of the spine and consists of 7 cervical vertebrae. There are intervertebral discs between all vertebral bodies. With their high water content, they buffer the pressure between the vertebral bodies.
Causes of Middle and upper back pain
Usually cervical and upper back pain are caused by muscle tension in the thoracic and/or cervical spine and in the adjacent areas. These tensions arise mainly from sedentary lifestyle. Without movement the upper back and neck become stiff, with the muscles there being permanently tensed. At the same time, the pressure on the neck and chest muscles increases at the front.
We are made to move, movement is the main engine of our body. Every chemical reaction, every process in our body happens thank to movement. Cells need contractions to speed up their methabolic reactions, organs like heart or lungs or stomach need movement to work. The lack of movement is therefore the main cause of diseases and pain in our body, included cervical and back pain. It is more important to focus on our sedentary lifestyle than on our posture! Let’s answer to this question: how many times, during your working day, do you stand up and take a 30 seconds walk? If the answer is “less than ten”, and you have back pain, you’ll already know why you feel bad.
There is no scientific correlation between “poor posture” and the onset of pain, so let’s focus more on the fact that you have to change posture frequently.
 What types of back pain are there and how can they be relieved?
What types of back pain are there and how can they be relieved?
Even if you have a perfect sitting posture, maintaining it for two to three hours straight is not better than maintaining a bad posture. The result is the same: muscle stiffness, blood flow restriction, and pain.
The muscles between the ribs (intercostal muscles) tighten, shrinking the chest cavity. This increases pressure on the joints, intervertebral discs, diaphragm and sternum. The result is pain in the middle and upper back and restricted mobility, including shallow breathing.
- Cause
-
For cervical and upper back pain, medical professionals often diagnose thoracic spine syndrome or cervical spine syndrome. Both syndromes combine various causes and symptoms for complaints in the upper back and in the neck region. The most common triggers for back pain in the thoracic and cervical spine include:
- Incorrect strain (e.g. frequent, long sitting, bent forward posture, “Mobile phone neck”)
- Lack of movement
- Whiplash (cervical spine due to a trauma) - Physical causes
-
In addition to the before mentioned triggers, the following causes can cause pain in the neck and upper back:
- Blockages of the costal joints
- Degenerative changes (on intervertebral discs, vertebra rib joints and ligaments)
- Disc herniation (prolapse) or bulging (protrusion)
- Fibromyalgia (pain syndrome)
- Misalignments of the spine (e.g. scoliosis, Scheuermann’s disease)
- Rheumatic diseases (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis/Bechterew’s disease, psoriatic arthritis, costochondritis)
- Thoracic vertebra fracture (e.g. after an accident)
- Osteoporosis (e.g. vertebral collapse)
- Joint wear (osteoarthritis)
- Flu-like infections
- Reflux (heartburn)If muscle tension, blockages, misalignments and degenerative changes in the spine as well as rheumatic diseases and reflux can be ruled out as the primary cause of pain in the middle and upper back, the following causes could also be present. In any case, these diseases should be determined promptly by a doctor:
- Organ diseases
- Tumours in the upper back area
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pneumonia
- PleurisyYou can find more information on the triggers and causes of neck pain here:
- Psychological triggers and intensifiers
-
Psychological factors can trigger and intensify upper back pain. Persistent stress and mental overloading ensure constant tension in the muscles. Anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorders and depression can also lead to increased muscle tone and therefore tension. In addition, we are often more aware of pain when we are not feeling well psychologically. If pain in the middle and upper back does not respond to common therapeutic approaches, it could also be due to a psychosomatic illness (a disease that has both organic and psychological causes) or a somatoform disorder (physical symptom for which no organic cause can be found).
Symptoms for pain in the middle and upper back
Middle and upper back pain can appear in isolation in the thoracic or cervical spine or radiate to adjacent regions such as shoulders, arms or head. Persistent thoracic and cervical spine pain can also be accompanied by sensory disturbances. In many cases the mobility of the affected parts of the spine is reduced. The following symptoms of middle and upper back pain may occur:
- Dull, pressing, or stabbing pain in the upper back
- Pulling or burning pain between the shoulder blades
- Pain which radiates to the chest, shoulders and arms
- Pulling or burning neck pain (cervical neuralgia)
- Pain that radiates into the head (tension headache or migraine)
- Dizziness or visual disturbances
- Sleep disorders
- Sensory disturbances (tingling and stinging/numbness/paralysis in the arms)
- Pain during heavy exertion or sport
- Feeling of permanent tension in the upper back muscles
- Feeling of constant blockage in the upper back and neck
- Limited mobility, stiff neck, stiff shoulder
- Breathlessness or pain when breathing
- Cracking noises in the thoracic or cervical spine and in the sternum
Learn more about symptoms of neck pain here:
12 + 7 vertebrae
As a rule, the thoracic spine has 12 and the cervical spine 7 vertebrae. This means that the middle and upper back consists of a total of 19 vertebrae. The cervical vertebrae are the smallest vertebrae in the spine and allow a lot of mobility. The 12 pairs of ribs of the thorax are attached to the 12 larger thoracic vertebrae.
Caution: Sudden pain in the middle, upper back and chest as well as tightness in the chest, shortness of breath, nausea, sweating, or transmission into the arms, jaw and neck can indicate a heart attack. If you suspect it, please call the emergency doctor immediately!
In the event of sudden pain in the cervical spine and neck accompanied by fever, cramps, severe headaches, paralysis, nausea, sensitivity to light, drowsiness, impaired consciousness or rigid neck, the emergency doctor must also be called immediately.
Painful areas
Middle and upper back pain can affect different areas. Centre, right or left – the position in which the upper back pain occurs may reveal something about an underlying pathological cause. More often, however, middle and upper back pain is due to muscle tension or joint blockages or nerve irritation.
- Causes of side pain in the middle and upper back
-
Back pain in the middle and upper back on the left or right can indicate organic diseases. Kidney diseases such as pelvic inflammation or kidney stones and pancreatitis can be associated with back pain. If the pain is accompanied by symptoms such as fever, fatigue, painful urination, nausea, loss of appetite and/or colic-related cramps, you should consult a medical professional as soon as possible. A urine, blood and ultrasound examination can quickly reveal whether the middle and upper back pain is an inflammation of the organs or another disease that requires treatment.
Middle and upper back pain that occurs on the right or left side can have the following triggers or causes:
- One-sided muscle tension due to one-sided strain
- Lateral joint wear
- Nerve root or nerve irritation on the right or left
- Unilateral joint blockage
- Inflammation of the renal pelvis (often accompanied by fever, painful urination and unilateral flank pain)
- Kidney stones/renal colicBy the way: Herniated discs in the thoracic spine are less common than in the lumbar and cervical spine. In the case of lateral pain in the middle back, muscular tension and strains are far more common. Nevertheless, if the back pain in the middle area persists other causes should be medically excluded. This is especially true if the pain radiates into the arms and leads to neurological complaints such as tingling and numbness.
- Causes of central pain in the middle and upper back
-
Pain in the middle and upper back that is felt in the middle can also often be attributed to muscle tension. However, if the pain radiates in a belt-shaped manner from the upper abdomen to the back, it can be an acute pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). In this case, you should seek medical help immediately. Another disease that must be clarified medically is bacterial or rheumatic inflammation in the area of the vertebral bodies (spondylodiscitis).
- Causes of pain in the middle, upper back and chest
-
Middle and upper back pain that pulls into the chest is mostly muscular
If the muscular tension affects the diaphragm, breathing may be restricted. In the case of very strong tension, it can even lead to a one-sided elevated diaphragm, which can affect other organs such as the stomach and oesophagus and thereby promote gastroenterological complaints such as reflux (heartburn). When stomach acid travels up the oesophagus, it often causes a painful burning sensation in the oesophagus that is perceived as chest pain.
In the case of sudden severe pain in the middle and upper back and chest, a heart attack should also be considered. In this case, please notify the emergency doctor immediately!
- Causes of pain in the upper back and shoulder blades
-
In the shoulder-arm syndrome (cervicobrachialgia) there is pain and also movement restrictions in the shoulder and arm, which are caused by the cervical spine. These complaints can arise as a result of mechanical stress (e.g. heavy carrying on one side), disc damage, vertebral blockages, osteoarthritis, rheumatism, tumours or injuries such as whiplash. In addition to pain, abnormal sensations such as tingling and numbness as well as loss of strength can occur in the affected arm. In addition, the pain in the upper back and neck area can radiate to the back of the head.
- Pain in the middle and upper back when breathing
-
If pain occurs in the middle and upper back when breathing, there is often tension in the muscles between the ribs or in the diaphragm behind them. Intercostal neuralgia results in acute stabbing nerve pain between the ribs that is aggravated when breathing and coughing. Pain in the middle and upper back when breathing should always be evaluated by a doctor, as it can indicate more serious organic problems such as pneumonia, pleurisy, pneumothorax, or heart attack.
- Pain in the upper back when lying
-
If back pain occurs in the upper area when lying down or immediately after getting up, poor sleeping conditions are often responsible. In many cases, the pillow is too large or the hardness of the mattress is not tailored to the individual physique. If you have problems with your lower back, it is advisable to sleep on your side, with a pillow between your knees. Keep your legs flexed and place a small pillow under your head to avoid kinking their cervical spine.

Treatment for pain in the upper back
For middle and upper back pain that is triggered by tension, there are a number of therapeutic approaches and household remedies that you can use to relieve the symptoms yourself at home. Professional help from physiotherapy and other disciplines can also help you loosen and stretch shortened and tense muscles in the upper back and optimise your posture and everyday movements in the long term in order to prevent pain in the middle and upper back.
Heat therapy
Heat is a very effective and at the same time a drug-free treatment method for tension-related pain in the middle and upper back. Traditional home remedies such as hot water bottles, cherry stone-filled cushions or heating pads usually relieve back pain quickly. However, these heat applications are often difficult to attach to the middle and upper back area or allow little freedom of movement during use. It is different with ThermaCare® HeatWraps: These can be attached directly to the areas to be treated and, depending on the product, can give off constant deep heat of approx. 40°C for 8 hours. The heat wraps can be worn comfortably anywhere, at home, at work and on the go. The ThermaCare® variant for the neck and shoulders is particularly suitable for pain in the upper back, the ThermaCare® variants for larger pain areas (Flex xl) and ThermaCare® for pain points (Flexible) are ideal for pain in the middle back.
Here you can learn more about how deep heat can relieve tension-related pain in the middle and upper back.
-

THERMACARE® For larger painful areas
to treat pain in upper leg, middle and upper back
Massages to relieve pain in the upper back
Since the thoracic spine is a part of the body that you can usually hardly reach with your own hands, massages are very suitable here to loosen the muscles and relieve tension-related back pain. The pressure stimuli that are given to the tissue during a massage help to loosen muscle hardening and can therefore support the blood circulation and recovery of the muscles. Choose a massage method that treats your symptoms with a combination of wellbeing and intensity that is good for you. Applying heat before, during or after the treatment can make the massage more effective. The use of pain-relieving ointments or oils that promote blood circulation can also help relax the muscles suffering from pain in the middle and upper back.
Physiotherapy
In the case of pain in the middle and upper back, methods from physiotherapy (manual therapy, chirotherapy / chiropractic, osteopathy, etc.) can relieve muscle tension and joint blocks. Before the treatment, ask a doctor to determine which form of therapy is best suited to your needs. If chronic pain in the middle or upper back is caused by a sedentary lifestyle, for example at work, occupational therapy can help identify and change everyday movement patterns so that the work environment can be better.

Pharmacological therapy
Non-steroidal pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen and diclofenac, or analgesics like acetaminophen, can provide short-term relief from middle and upper back pain. Muscle relaxants can also be used for very severe middle and upper back pain. When using medication, caution should be exercised, as medication can have side effects or can trigger interactions with other substances. Some prescription muscle relaxants are even addictive. Please note that although you can achieve temporary pain relief with medication, this does not eliminate the cause of the pain in the upper back area. Especially with chronic middle and upper back pain, after excluding treatable physical causes, you should train your muscles over the long term and work on correct posture.
Movement for middle and upper back pain
Back-friendly yoga, back exercises, and exercises that stretch and loosen muscles and fasciae help to relieve and prevent pain in the middle and upper areas of the back. The following applies to tension-related pain: Exercise helps! Rest is not our best option. It is best to train your muscles for a few minutes a day for a stable and at the same time flexible back. Make sure that you adhere to the recommended motion sequences and do not overload The body. In this way tensions can be released and the muscles can regenerate. This not only relieves pain in the middle and upper back, the entire body can benefit from training tailored to your needs.
Acupuncture and acupressure
Acupuncture involves placing needles, while acupressure involves applying pressure to specific points. Both can help relieve tension in the muscles in the case of back pain in the middle and upper area. Acupuncture points are also treated on parts of the body such as the ear or foot, which are reflexively related to the painful areas in the middle and upper back. The teachings of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) on which acupuncture is based treat chronic pain in the middle and upper back using other methods such as diet, herbs and exercise.
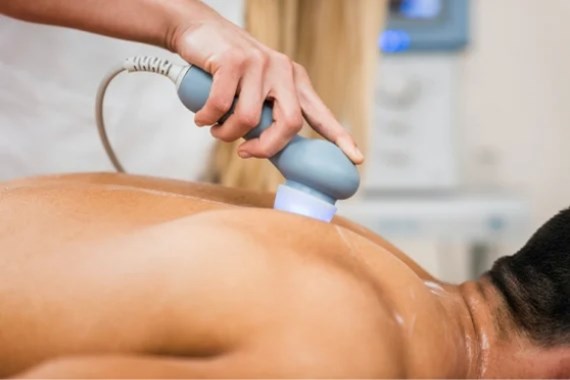
Stimulation current and ultrasound
Ultrasound and TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) can provide relief from pain in the middle and upper back. With ultrasound therapy, the tissue is heated, which stimulates blood flow and metabolism in the muscles. With TENS therapy, a small TENS device is attached to the painful area. This releases low-threshold stimulation current into the muscles, which is intended to reduce the perception of pain. TENS devices can be prescribed by a doctor for pain in the middle and upper back.
Cold therapy for pain in the middle and upper back
Pain in the middle and upper back caused by acute inflammatory processes (24 to 72 hours) or an injury may be better treated with cold rather than with heat. Cooling pain gels, cold gel compresses, cool packs or a cold shower are suitable for this. Although cold is a good pain killer, it hasn’t draining properties used alone. If your main issue is drainage we recommend you to use compression techniques. In the case of inflammation and injuries, a doctor should clarify what kind of treatment is indicated for pain in the middle and upper back.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
- What can be done about middle and upper back pain?
-
Middle and upper back pain or pain in the cervical and thoracic spine can be relieved with a number of measures. For tension-related pain in the middle and upper back, heat therapy, exercise, massage, physiotherapy, analgesics, ultrasound and acupuncture can help. Cold therapy may also be indicated for middle and upper back pain in the case of acute inflammatory process after, for example, an injury. Please have a doctor determine the cause of the pain in the thoracic and cervical spine before starting therapy.
- What helps to relieve middle and upper back pain?
-
Rapid relief from pain caused by muscle tension in the cervical and thoracic spine is provided by heat applications such as ThermaCare® HeatWraps, sauna or red light, stretching exercises for shortened muscles, certain massage techniques as well as analgesics.
- What does middle and upper back pain mean?
-
The lack of movement is therefore the main cause of diseases and pain in our body, included cervical and back pain. It is more important to focus on our sedentary lifestyle than on our posture! Let’s answer to this question: how many times, during your working day, do you stand up and take a 30 seconds walk? If the answer is “less than ten”, and you have back pain, you’ll already know why you feel bad.
Other causes of pain in the thoracic and cervical spine (thoracic spine/cervical spine) are:
- Blockages of the costal joints
- Degenerative changes (on intervertebral discs, vertebral/rib joints, ligaments)
- Disc herniation (prolapse) or bulging (protrusion)
- Fibromyalgia (pain syndrome)
- Misalignments of the spine (e.g. scoliosis, Scheuermann’s disease)
- Rheumatic diseases (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis/Bechterew’s disease, psoriatic arthritis, costochondritis)
- Thoracic vertebra fracture (e.g. after an accident)
- Osteoporosis (e.g. vertebral collapse)
- Joint wear (osteoarthritis)
- Whiplash (on the cervical spine)
- Flu-like infections
- Strains
- Organ diseases
- Tumours in the upper back area
- Reflux (heartburn)
- Pneumothorax
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pneumonia
- Pleurisy