Muscle tension
Humans have over 650 muscles in their bodies. Over 600 muscles belong to the skeletal musculature. This is where the muscle tension that we perceive as painful occurs. What happens when there is tension?

Contents:
What is muscle tension?
First of all, muscles can become tense as part of their normal function. The muscle shortens and blood flow decreases. If the muscle is relaxed again afterwards, the blood flow increases. However, if the muscle is tensed for a long period of time or even constantly, the muscle will permanently shorten. This is no longer supplied with sufficient blood and can harden as a result. The sensitivity of the pain receptors within the muscle is increased and the nerves in and around the muscles get irritated.
Tension
Most of all back complaints are caused by malfunctions and tension in the muscles.
Typical symptoms
The typical symptoms of muscle tension are dull or pulling pain that can radiate to other muscle groups or parts of the body (e.g. tension related headache) and can restrict mobility.
Causes: How does muscle tension arise?
Causes: How does muscle tension arise?
Muscle tension is common and affects people of all ages. There are numerous reasons for this:
- lack of movement
- one-sided posture and incorrect loading of the spine
- overloading
- magnesium deficiency
- psychological factors
If we move too little, our muscles are insufficiently trained, and an imbalance occurs between individual muscle groups. Sedentary lifestyle or incorrect loading also have a stressful effect on the muscles. These then lose flexibility and stability.
This results in a vicious cycle: Due to the muscle tension, we instinctively adopt a protective posture to avoid the pain. This increases muscle stiffness. If this vicious circle continues over a longer period of time, pain could become chronic. And that in turn aggravates the muscle tension again.
Magnesium deficiency can also trigger muscle cramps and tension.
Psychological causes of muscle tension
Psychological causes such as constant stress, emotional stress, anxiety disorders and depression are another trigger or intensifier of muscle tension, because they ensure a permanently increased muscle tone. Many people do not even notice that they raise their shoulders or tense their back muscles when they feel tense or anxious until they experience pain or other symptoms of muscle tension. In addition, many mental illnesses are often accompanied by a tense or slumped posture, disturbed body perception or a more intense sense of pain. In addition to the psychological symptoms, there is a vicious circle of tension, pain and posture, which in turn affects the psyche.
How can muscle tension be released?
There are several measures and home remedies that can be used to relieve muscle tension in the short term to give the muscles a break. Because when the tension is released, the pain is reduced. What measures help quickly against muscle tension and how can you relieve tension yourself?
Heat for tension
If heat acts on the tense muscle, the transmission of the pain stimulus in the tissue is inhibited, blood circulation is stimulated and the perception of pain decreases. This allows the muscle to loosen up, hardenings and tensions are released. That’s why heat is a good way to relieve muscle tension quickly and naturally, and even to relieve it yourself.
Studies have shown that applying heat directly to the tense muscle at a low temperature and for several hours increases the temperature even at a depth of two centimeters. ThermaCare® products provide this continuous heat supply at a constant temperature. As they can be attached directly to the painful areas and deliver deep heat continuously for 8 hours they are ideal for heat treatment of tension in the back, neck and shoulder area. ThermaCare® HeatWraps can be worn discreetly under clothing and allow heat to be combined with movement - a combination that can relieve muscle tension even better.
In addition to heat wraps, there is a whole range of home remedies that you can use to relieve tension yourself including from hot water bottles to electric heating pads to infrared lamps.
You can find more information about heat therapy for muscle tension here:
Please note: While heat is good for muscle tension, it is not advised for muscle pain associated with oedema or hematoma or inflammation. Cold usually works better in the first 24 to 72 hours from the onset. If you are not sure about the cause of the muscle pain, please have a doctor clarify if the discomfort is due to tension.
Medicinal help for muscle tension
Conventional painkillers and anti-inflammatories such as Ibuprofen and Diclofenac as well as the analgesic Paracetamol relieve the pain in the short-term, but can only be taken for a short time. In addition, as with medicines in general, side effects can occur with these medicines.
Muscle relaxing drugs (central muscle relaxants) can be used for very strong or chronic tension. They have a dampening effect on muscle tone. Since they usually have strong side effects and sometimes even potential to become addictive, they are used after medical consultation and only in cases of severe symptoms.
Pain ointments with an active pharmaceutical ingredient are applied directly to the painful area. From there, they penetrate the muscle tissue, where they exert their analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect directly at the centre of the pain. They can also cause side effects, e.g. local skin reactions.
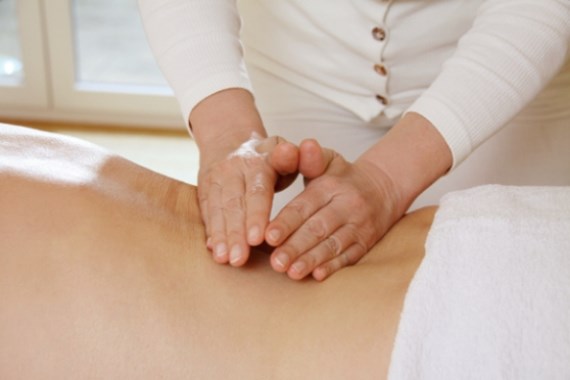
Massage for tension relief
Massages are a popular measure against muscle tension. During a massage, depending on the technique, gentle or stronger pressure is applied to the muscles, focusing on particularly painful trigger points in the tissue. The blood circulation is stimulated and superficial tensions can be released. Some massage techniques provide a pleasant wellness effect, others are intense and even painful. Since not every massage is suitable for every problem, you should find out beforehand how the chosen technique works and whether it is effective for your own complaints.
-

THERMACARE® For neck and shoulder and wrist
for the treatment of neck, shoulder and wrist pain
How can muscle tension be prevented?
A strenuous day in the office, a long drive in the car, or if the body is under constant stress, acute tension recurs or can even become chronic. What can you do to prevent muscle tension?
- Movement for tension relief
-
The most important measure is certainly to train and strengthen the muscles through regular exercise. In the case of chronic tension, it is not advisable to start strenuous strength training without preparation, which could overwhelm the muscles. Rather, untrained people should first stretch the muscles specifically with individual exercises and strengthen neglected muscle parts. The aim is to build flexible and stable muscles that can withstand unavoidable stress.
In addition to the exercises, it makes sense to practice sport such as swimming, yoga, Pilates or Nordic walking. Combined with stretching, these activities can counteract the hardening and shortening of muscles.
- Sedentary lifestyle and muscle stiffness
-
Since chronic muscle tension can in many cases be traced back to a sedentary lifestyle, it is certainly also beneficial to work on your own daily routine.
You don’t need to think about complex exercises to do, let’s keep it simple: stand up every 30 minutes and take a short walk, from your desk to the office door, and then turn back to your seat. You’ll find that it will be very helpful for your back pain and will also prevent it. You can turn on the alarm clock on your smartphone or pc, or write on a post it “stand up every 30 minutes”. Do it every day, you’ll feel really better!
Having a sport routine outside from work is also a good way to manage and prevent back pain. Don’t be afraid about the kind of sport you’d like to practice, the secret here is optimal loading. Try to gradually practice the sport you like, for the first month not more than twice a week, and then you can increase the frequency.
You can also work on your body awareness. Here we present you a selection of methods you can use to work on your body perception:
- Cantienica: The Cantienica® method was developed by the Swiss journalist Benita Cantieni. She teaches a holistic uprightness training based on mindful self-awareness that alleviates and positively influences posture. The focus here is on tensioning the spine and pelvic floor training.
- Feldenkrais: The Feldenkrais Method, founded by the Israeli Jiu-Jitsu teacher Moshé Feldenkrais, focuses on increasing mobility by making people aware of unfavourable movement patterns and dissolving them in favour of more favourable, energy-saving movement sequences.
- Alexander: The Alexander Technique, developed by the Australian actor Frederick Matthias Alexander, also focuses on raising awareness and changing habits that lead to painful muscle tension and restricted movement. A special focus here is on the flow of breath.
- Bio-Feedback: With the help of this method, interested Patients learn to consciously relax their muscles and achieve a better body feeling through the electronic visualisation of their muscle tension in combination with relaxation exercises.
You can find some tips on relaxation techniques that can help with tension in our neck section.
- Magnesium for muscle tension
-
Do you often suffer from muscle cramps? Then your tension could also be due to a magnesium deficiency. Magnesium is involved in many processes in the body and contributes to normal muscle function, among other things. Magnesium deficiency can manifest itself in muscle spasms and tension, exhaustion and a lack of concentration, cardiac arrhythmias, and dizziness. With a one-sided diet, increased physical activity, stress and chronic intestinal diseases, the magnesium content in the blood can be too low and lead to increased tension. If this should be the case, you can supplement magnesium with a vitamin preparation, magnesium oil or through your diet.
Many foods contain magnesium. Good natural sources of magnesium are walnuts, almonds, sunflower seeds, oatmeal, whole grain products and soybeans.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
- What helps with muscle tension?
-
In the case of muscle tension, heat applications (such as ThermaCare® HeatWraps, sauna or heating pads) and massages provide quick relief. In the short term, you can also treat it with anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, or pain ointments. Regular exercise, loosening exercises and targeted muscle training or relaxation training have a preventive effect against muscle tension.
- How long does muscle tension last?
-
In most cases, tense muscles recover within a few days. In the case of chronic or severe muscle tension, however, regeneration can take considerably more time.
- Which painkillers help with muscle tension?
-
For acute muscle tension, over the counter and prescription painkillers, such as anti-inflammatory drugs or muscle relaxants, can be used to reduce the pain. If the symptoms are very severe, muscle relaxants can be used after medical consultation. However, these can have strong side effects.
- How does muscle tension arise?
-
If a muscle is permanently tensed without being able to recover, tension develops. The muscle is no longer well supplied with blood, it hardens and shortens. The sensitivity of the pain receptors within the muscle is also increased and the nerves become increasingly irritated. Causes of permanent muscle tension can be:
- lack of movement
- unfavorable (monotonous) movement patterns
- overloading
- magnesium deficiency
- psychological factors
- Sociological factors - Does heat or cold help better with tension?
-
Stiff muscles can be treated very well using heat applications (e.g. with the ThermaCare® HeatWraps). However, if the pain in the muscles is associated with oedema or hematoma or acute inflammation, the use of heat is not advisable. Cold is more suitable here, for example in the form of a cool pack or a cooling pain gel with an anti-inflammatory agent. Please clarify the cause of the muscle pain with a doctor before the treatment.
- Why does heat help relieve muscle tension?
-
When heat acts on the tense muscle, the transmission of the pain stimulus in the tissue is inhibited, blood flow is stimulated and pain perception is reduced. This allows the muscle to relax and loosen up, hardening and tension are released.